Select Characteristics Exhibited by the Glycocalyx of Eukaryotic Cells
Like prokaryotes eukaryotic cells have a plasma membrane made up of a phospholipid bilayer with embedded proteins that separates the internal contents of the cell from its surrounding environmentA phospholipid is a lipid molecule composed of two fatty acid chains a glycerol backbone and a phosphate group. On bacterial cells the glycocalyx provides a protective coat from host factors.

Microbiology Module 3 Flashcards Quizlet
Please select characteristics exhibited by most protozoans.

. Organisms of the kingdoms Plantae Animalia Protista and Fungi are all eukaryotes. Outermost surface of cell Composed of protein Co Outermost surface of cell Composed of protein Co Q. Select characteristics exhibited by the glycocalyx of eukaryotic cells.
Eukaryotic cells have the nucleus enclosed within the nuclear membrane. One turn or cycle of the cell cycle consist of two general phases. These include vesicles the endoplasmic reticulum and.
Figure 339. Biology Science Microbiology BIO 257. Select characteristics exhibited by the glycocalyx of eukaryotic cells.
First archaeal membrane phospholipids are formed with ether linkages in contrast to the ester linkages found in bacterial or eukaryotic cell membranes. When on eukaryotic cells the glycocalyx can be a factor used for the recognition of the cell. Motile by means of flagella cilia or pseudopodia.
Eukaryotic cells have a nucleus surrounded by a complex nuclear membrane that contains multiple rod-shaped chromosomes. A cell wall is the outermost layer of the eukaryotic cells. Interphase and the mitotic phase.
Composed of polysaccharides. It envelopes the cell membrane protecting the cell from changes in osmotic pressure Figure 315Osmotic pressure occurs because of differences in the concentration of solutes. Some microorganisms are composed of prokaryotic cells whereas others are composed of.
1 All plant cells and animal cells are eukaryotic. The glycocalyx of bacteria can assume several forms. The cells divide by a process called mitosis.
Bacteria and Archaea are all prokaryotes. Prokaryotes are organism with a nucleus that is not enclosed within a membrane. A thin protective structure loosely bound to the cell wall that protects the cell against drying helps trap nutrients and sometimes binds cells together Endosymbiotic Theory Holds that the organelles of eukaryotic cells arose from prokaryotes that came to live in a symbiotic relationship inside the eukaryote-to-be cell.
Eukaryotic cells have evolved an endomembrane system containing membrane-bound organelles involved in transport. The eukaryotic cell cycle is an ordered and carefully regulated series of events involving cell growth DNA replication and cell division to produce two clonal daughter cells. Motility unicellularity presence of a nucleus and a variety of other organelles eukaryotic heterotrophic nutrition and a size range from 3 300 µm.
They are informally grouped together because most share the following characteristics. Outermost surface of the cells. The glycocalyx is a thick outer covering of the plasma membrane.
The cell has mitochondria. The result is a. In most prokaryotic cells morphology is maintained by the cell wall in combination with cytoskeletal elements.
Contain a nucleus and variety of organelles. Please select characteristics exhibited by most protozoans. Second archaeal phospholipids have branched chains whereas those of bacterial and eukaryotic cells are straight chained.
First archaeal membrane phospholipids are formed with ether linkages in contrast to the ester linkages found in bacterial or eukaryotic cell membranes. Outermost surface of cell Composed of protein Composed of polysaccharide Means. Cell walls containing cellulose.
Eukaryotes are those organisms with a clearly defined nucleus enclosed in a membrane. Flagella and cilia are the locomotory organs in a eukaryotic cell. Composed of protein means of locomotion Select characteristics exhibited by.
Means of adhering to other cells and surface. It is composed of strands of sugars and proteins bound together. 3 µm - 300 µm size range.
The cell wall is a structure found in most prokaryotes and some eukaryotes. The possession of a glycocalyx on bacteria is associated with the ability of the bacteria to establish an infection. Eukaryotic cells contain 80S ribosomes in the rough endoplasmic reticulum membrane bound-ribosomes and cytoplasm free ribosomes.
Select the characteristics exhibited by glycocalyx of eukaryotic cells check all that apply. They contain 70s ribosomes in mitochondria and chloroplasts. -outermost surface cells -composed of protein -composed of polysaccharides -means of adhering to other cells -means of locomotion -signal reception.
Characteristics of Eukaryotic Cells. Select characteristics exhibited by the glycocalyx of eukaryotic cells Outermost surface of the cell composed of polysaccharide means of adhering to other cells and surfaces signal reception. Second archaeal phospholipids have branched chains whereas those of.
Select characteristics exhibited by the glycocalyx of eukaryotic cells.

Microbiology Module 3 Flashcards Quizlet

Microbiology A Systems Approach 2nd Ed Ppt Video Online Download
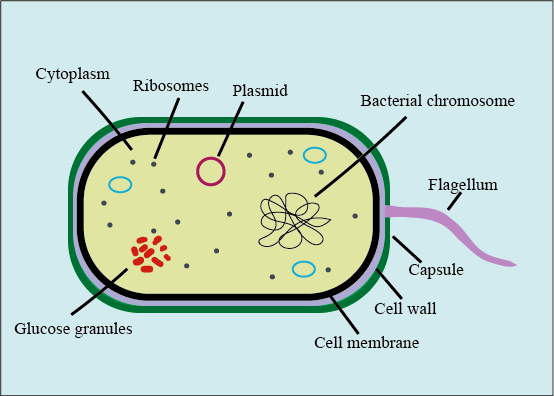
The Term Glycocalyx Is Used For A The Cell Wall Of Class 11 Biology Cbse
No comments for "Select Characteristics Exhibited by the Glycocalyx of Eukaryotic Cells"
Post a Comment